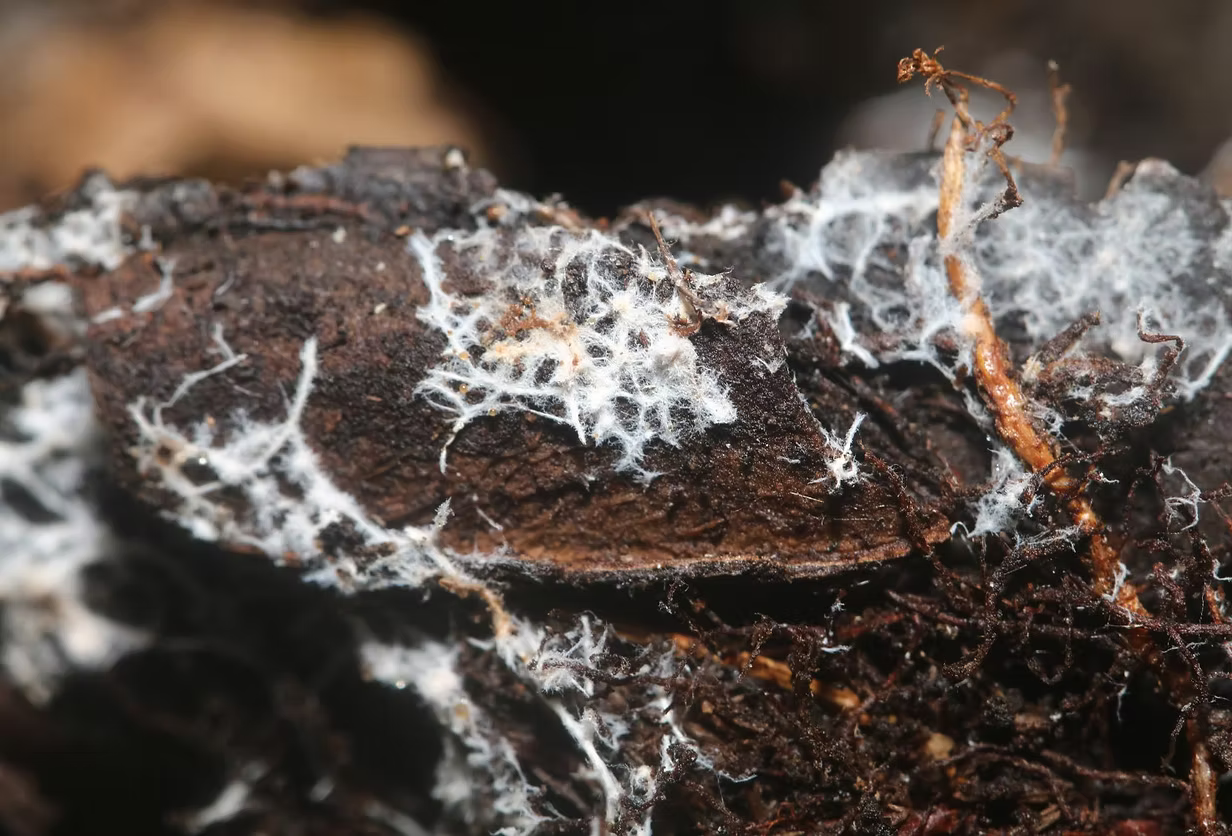

Friendly fungi: Mycorrhiza
A true hero lurks beneath the earth: a delicate network of fungal filaments that lives in the soil and forms a valuable symbiotic relationship with plants – the so-called mycorrhiza. This natural partnership promotes root growth, improves nutrient uptake, and strengthens plants from the ground up.
Mykos = fungus, Rhiza = root
Mycorrhizae are special root fungi that form a close symbiotic relationship with the fine roots of plants. This relationship offers numerous advantages:
Better nutrient uptake: The fungi's fine hyphal network increases the absorbent surface of the roots by 100 to 1,000 times. This allows plants to absorb water and important nutrients such as phosphorus, nitrogen, potassium, magnesium, and iron more efficiently.
Increased resilience & vitality: By releasing enzymes and organic acids, mycorrhizae improve the availability of micronutrients. This strengthens the plant and increases its resistance to stress, drought, disease, and adverse site conditions.
Healthy growth & fewer failures: Stronger roots, better growth of new plantings, lower failure rates, higher vitality
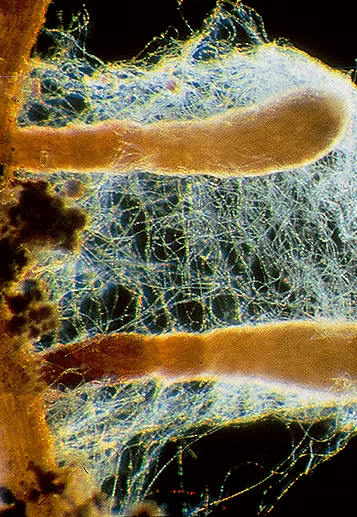
Whether trees, shrubs, vegetables, lawns, or flowers – around 90% of all plants benefit from mycorrhiza . For many, it is even vital for their survival: Without this symbiosis, species such as fir, spruce, beech, and oak could not exist. Birch, willow, pine, and roses also require it for vigorous growth. Mycorrhiza has been established in Germany since the 1970s and has long been standard for large trees. Its application is simple: in the planting substrate, over a large area before soil cultivation, or injected directly into the root zone.
The result: up to 1000× higher nutrient uptake , better supply of phosphate, potassium & Co. – for healthy, stress-resistant plants in a natural way.
What types of mycorrhiza are there?
-
Endo-mycorrhiza
The term "endo" means "inside": Endo-mycorrhizal fungi penetrate the root tissue of the plant and form finely branched structures through which water and nutrients are efficiently absorbed. This form is invisible to the naked eye because it does not form above-ground fruiting bodies, but it works directly inside the root.
-
Ecto-mycorrhiza
In ectomycorrhiza, fungal hyphae surround the root from the outside without penetrating the cells. This type is often visible – for example, as the fruiting bodies of fly agaric, porcini, truffles, or puffballs. Nutrient exchange takes place in the contact zone between the fungus and the root – without entering the cell interior.
Mycorrhiza Finder
Find the mycorrhiza type of your plantWhat type of mycorrhiza does your plant need?
We've created a handy app for you that lets you find out in seconds. Simply enter the plant name and search.
We've created a handy app for you that lets you find out in seconds. Simply enter the plant name and search.
How does the application work?
-

In pots or when planted individually
Mix into the planting substrate
-

Area application
Before mechanical soil cultivation (e.g. forestry, lawn, ...)
-

Injection using a geoinjector
During site remediation, directly into the root zone via soil aeration with compressed air .
Do you want to increase your yield with mycorrhiza?
Our sales team will be happy to assist you! Our team is here to help and will quickly find the right solution for your needs.
With Arboboost, you rely on sustainable soil improvers that not only strengthen your plants but also contribute to the long-term health of soils and the environment. Whether it's fruit, vegetables, trees, or green spaces – we'll accompany you on your path to fertile growth. We look forward to hearing from you!





